Industries today require high-capacity storage devices to meet their growing need to process and retain data. High-density storage units are becoming more popular for their expanded capacity. Many of these are made with NAND flash. There are several types of NAND flash, each having different properties and advantages: SLC (Single-Level Cell), MLC (Multi-Level Cell), and TLC (Triple-Level Cell).
The figure below highlights the characteristics of different NAND flash types. Each pie represents a single storage cell. So in SLC, one bit of data is stored on one cell, while in TLC, three bits are stored.
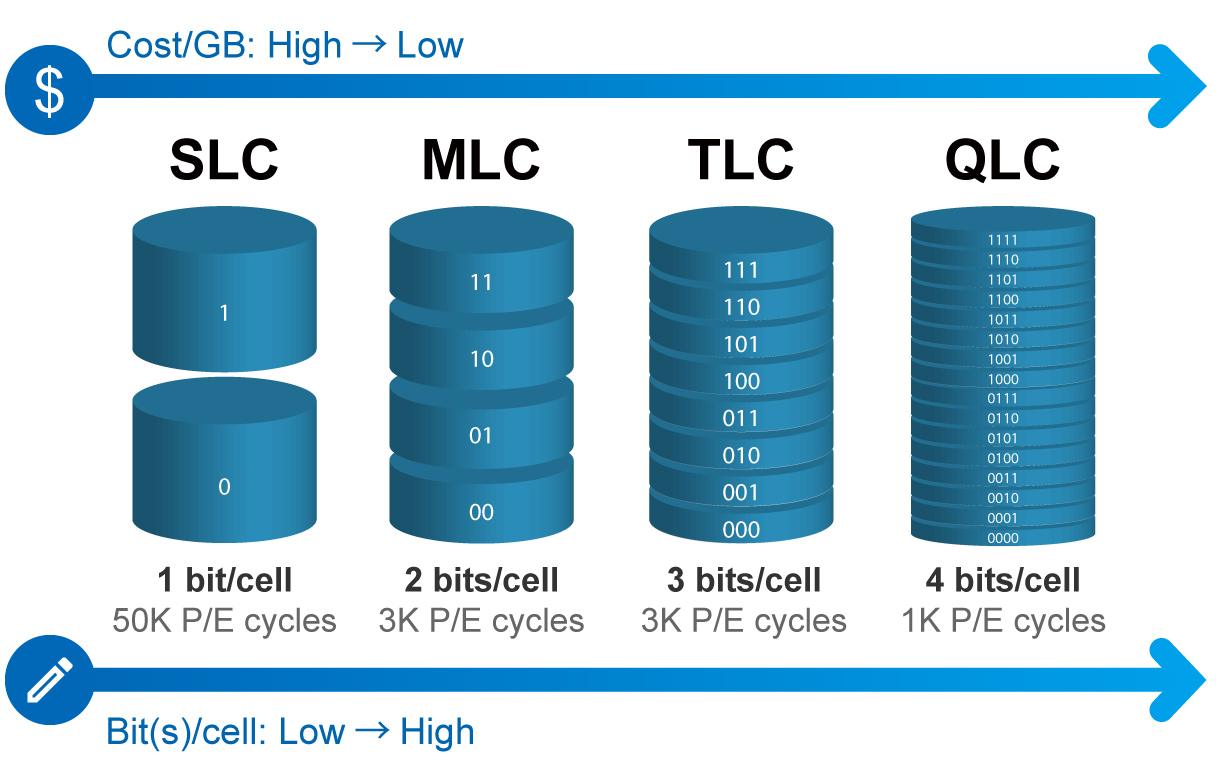
The difference between the three technologies is clear. SLC stores the least amount of data, but features the fastest read/write speeds. TLC is the opposite. To save the same amount of data, three times the number of SLC cells are needed as compared to TLC, greatly increasing the cost.
However, for most consumers, the desire for speed matches that for capacity. SLC cache* technology provides a balanced solution to meet this demand.
* This technology is used for TLC NAND flash.
SLC Cache
By dividing a segment within TLC to simulate SLC, transfer speeds within the segment will be temporarily increased. Once buffer space is full, speed will return to its original level.
SLC Mode
SLC Cache limitations mean this technology cannot fulfill the demand for constant read/write at high speeds. That being so, another technology that can transform TLC into SLC has come into play—SLC Mode. Unlike SLC Cache, there are no buffer zone restraints on SLC Mode, because each TLC cell acting under this mode processes only one bit of data—just like SLC cells. Hence space constraints are removed and high read/write speeds can be sustained.
Although storage capacity per cell is reduced in SLC mode, taking three times amount of cells in TLC to simulate SLC, the cost is dozens of times less than SLC. This makes SLC mode an enticing alternative for companies seeking high storage capacity, high speed, and low cost.
Conclusion
SLC and MLC have differing advantages when it comes to durability and data retention. SLC Mode solves the inherent limitations of TLC and offers better reliability than MLC—equivalent to SLC—at an advantageous cost. In short, SLC Mode is a new alternative solution just right for industrial applications.